Useful commands to see general information on the firewall resources been used, interface and traffic statistics, and traffic counters.
System and resources
show system resources is the same as top in linux, adding follow will keep it auto refreshing until stopped with CTRL + C.
ste@HME-PAL-OEW1> show system resources follow
top - 17:41:48 up 25 days, 9:26, 1 user, load average: 0.82, 0.43, 0.33
Tasks: 222 total, 2 running, 167 sleeping, 0 stopped, 1 zombie
%Cpu(s): 8.9 us, 1.7 sy, 0.0 ni, 87.0 id, 0.0 wa, 2.2 hi, 0.2 si, 0.0 st
KiB Mem : 6612900 total, 280932 free, 2637248 used, 3694720 buff/cache
KiB Swap: 4095996 total, 3526652 free, 569344 used. 886092 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
6592 root 20 0 66.7g 2.6g 2.6g S 15.9 41.0 5349:19 pan_task
5341 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 3.0 0.0 968:27.46 kni_single
5415 root 20 0 472768 25248 0 S 0.7 0.4 147:20.85 distributord
2924 root 0 -20 3047528 2.6g 2.6g S 0.3 40.8 61:20.15 masterd_apps
2967 root 15 -5 168604 7140 1988 S 0.3 0.1 64:58.25 sysd
5293 nobody 20 0 52840 2200 1632 S 0.3 0.0 19:50.62 redis-server
5298 nobody 20 0 50280 228 72 S 0.3 0.0 19:43.07 redis-server
5411 root 20 0 1764808 374444 122964 S 0.3 5.7 62:49.87 devsrvr
5416 root 20 0 520088 47852 208 S 0.3 0.7 45:03.03 iotd
5418 root 20 0 741304 150176 112504 S 0.3 2.3 218:54.33 useridd
5486 nobody 20 0 50280 2032 1640 S 0.3 0.0 30:57.99 redis-server
5493 nobody 20 0 58984 1708 1172 S 0.3 0.0 92:21.15 redis-server
5538 root 20 0 1745340 244996 12768 S 0.3 3.7 14:15.94 logrcvr
5547 root 20 0 721500 74572 9632 S 0.3 1.1 181:41.14 dnsproxyd
6889 root 20 0 66.7g 2.6g 2.5g S 0.3 40.5 8:04.76 sdwand
7061 root 20 0 66.7g 2.6g 2.5g S 0.3 40.5 63:38.55 pan_dha
8730 root 20 0 160764 15512 4 S 0.3 0.2 28:41.15 envoy
17075 ste 20 0 121636 2960 2400 R 0.3 0.0 0:00.04 top
28650 root 20 0 0 0 0 I 0.3 0.0 3:38.61 kworker/0:1-eve
1 root 20 0 4388 4 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:10.67 init
The running firewall processes and PID can be viewed using the command show system software status.
If running any tasks that are CPU intensive such as logging of the packet flows, this command is useful for keeping an eye on what resources are using up what percent of the CPUs. By default it will be for the last 60 seconds, can view the average and maximum CPU usage by filtering on the last 1-60 seconds, 1-60 minutes, 1-24 hours, 1-7 days or 1-13 weeks.
ste@HME-PAL-OEW1> show running resource-monitor hour last 3
ste@HME-PAL-OEW1> show running resource-monitor
Resource monitoring sampling data (per second):
CPU load sampling by group:
flow_lookup : 1%
flow_fastpath : 1%
flow_slowpath : 1%
flow_forwarding : 1%
flow_mgmt : 1%
flow_ctrl : 1%
nac_result : 0%
flow_np : 1%
dfa_result : 0%
module_internal : 1%
aho_result : 0%
zip_result : 0%
pktlog_forwarding : 1%
send_out : 1%
flow_host : 1%
send_host : 1%
fpga_result : 0%
CPU load (%) during last 60 seconds:
core 0 1
* 1
Both these commands provide really nice realtime statistics on session traffic (packet rate, throughput, number of sessions) and applications (sessions, packets, bytes) that keep refreshing until quit.
ste@HME-PAL-OEW1> show system statistics session
System Statistics: ('q' to quit, 'h' for help)
Device is up : 18 days 3 hours 12 mins 55 sec
Packet rate : 120/s
Throughput : 165 Kbps
Total active sessions : 61
Active TCP sessions : 37
Active UDP sessions : 21
Active ICMP sessions : 3
ste@HME-PAL-OEW1> show system statistics application
Top 20 Application Statistics: ('q' to quit, 'h' for help)
Virtual System: vsys1
application sessions packets bytes
-------------------------------- ---------- ------------ ------------
stun 1184 2581768 2093735764
itunes-base 3181 1823844 1698765716
twitter-base 936 1719312 1628091621
icloud-base 7005 1240232 910446082
rtp-base 3 735148 807039702
http-video 23 9402047 9396393333
avira-antivir-update 277 527288 537032712
A few useful commands for looking at the dataplane interface utilisation.
show interfaceall Interface name, speed, duplex, state, MAC, IP address and zone
show interfaceethernet1/1 Settings and traffic counters including transmitted, received dropped and errors
show counter interfaceall Traffic counters including transmitted, received dropped and errors
show counter rateethernet1/1 Number of tx/rx packets and Mbps for last second
Netstat shows information related to the management plane.
show netstat interfaces yesShows management, loopback and tap interfaces as well as counters (*all yes* also shows tcpdump
show netstat route yesShows the management routing table
show netstat all yesShow the ports open and the state of the connections on them
show netstat programs yesShows ports open anD connections but now includes program and PID
I dont really understand the purpose of the ‘system state’ commands yet, seem to be hardware capabilities as well as counters.
show system state filter-pretty sys.s1.p*Shows counters on all interfaces
show system state browserInterface stats in realtime, do Shift + L, port_stats, Y, U
Logs
System logs can viewed by severity and further filtered down based on the object, subtype and event. Juts like traffic logs can filter the time-frame and add csv-output equal yes to display the output in csv format.
show log system receive_time in [last-60-seconds | last-15-minutes | last-hour | last-6-hrs | last-12-hrs | last-24-hrs]
show log system receive_time in [last-7-days | last-30-days | last-calendar-day | last-calendar-month]
show log system start-time [equal | not-equal] <YYYY/MM/DD@hh:mm:ss>
show log system end-time [equal | not-equal] <YYYY/MM/DD@hh:mm:ss>
ste@HME-PAL-OEW1> show log system severity
> equal equal
> greater-than-or-equal greater-than-or-equal
> less-than-or-equal less-than-or-equal
> not-equal not-equal
ste@HME-PAL-OEW1> show log system severity greater-than-or-equal
critical critical
high high
informational informational
low low
medium medium
ste@HME-PAL-OEW1> show log system object equal "ethernet1/2" subtype equal "port"
Time Severity Subtype Object EventID ID Description
===============================================================================
2022/09/28 08:18:06 info port ethern link-ch 0 Port ethernet1/2: Down Unknown duplex
2022/09/28 08:18:06 info port ethern link-ch 0 Port ethernet1/2: Up 10Gb/s-full duplex
2022/09/28 08:18:06 info port ethern link-ch 0 Port ethernet1/2: MAC Up
The CLI doesn’t provide auto-completion on object, subtype or event, for this reason the GUI maybe a bit easier for looking at system logs.
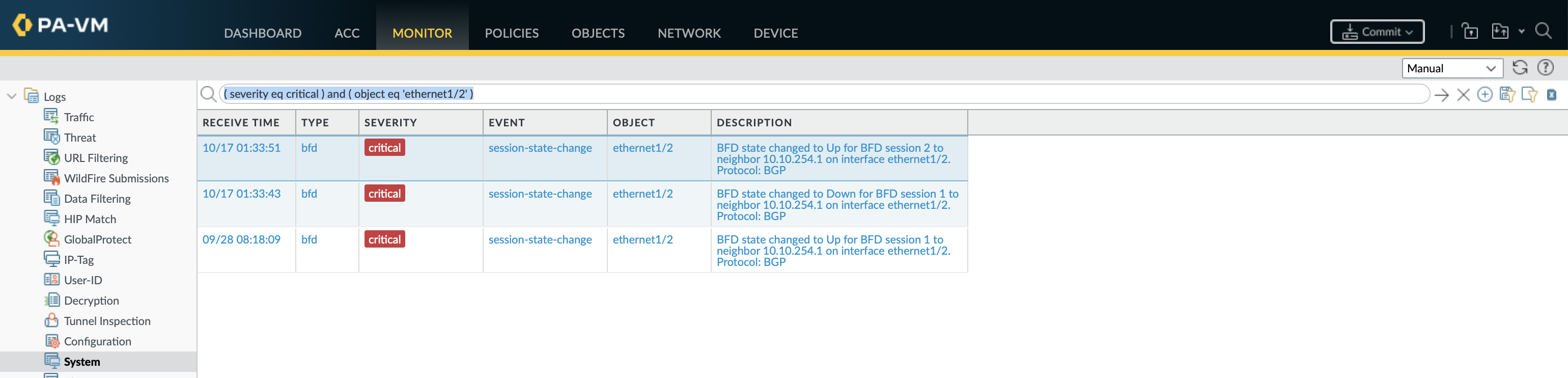
The majority of the other non-system logs are grouped under plugins-log and mp-log (dp-log on some platforms). To view and filter use tail, less, follow and grep.
ls mp-log? View all log files such as
ls plugins-log? View all log files for plugins
tail mplogpan_boot.log
less mp-logconfigd.log
less mp-logdhcpd.log
tail mp-logrouted.log
tail followyes mp-logbfd.log
tail followyes mp-logpan_ifmgr.log
A disk quota is assigned to the different log types, logs will be purged when the quota is exceeded. The allocated quota and current usage levels can be checked with the command show system logdb-quota.
Global counters
All sessions traversing the firewall are tracked by the processes that touch them with global counters incremented for each step that a packet takes and for each packet in a session. show counter global provides information about the processes/actions taken on the packets passing through the device; whether they are dropped, NAT-ed, decrypted and so on. This is a list of all the possible global counters.
ste@HME-PAL-OEW1> show counter global filter
+ aspect Counter aspect
+ category Counter category
+ delta Difference from last read
+ packet-filter Counters for packet that matches debug filter
+ severity Counter severity
+ value value
Global counters can be filtered based on severity, category and aspect.
- Severity: Are 4 levels of severity, info (default for all counters), drop (indicate something that was intentionally discarded like due to a security policy), error (packets that are malformed and are discarded), or warn (system level error or abnormality in received packets)
- Category: Indicates which process this counter is related to (dfa (APP-ID algorithm engine), appid, dlp, flowpacket, uid, zip, nat, etc)
- Aspect: More detail regarding which stage a packet was in when the counter was incremented (parse, session, and forward are three stages of flow)
Drop counters are normally the ones of real interests as it keeps a count of all drops, what is causing them (such as flow_policy_deny for packets that were dropped by a security rule) and how many packets were dropped. By running the command multiple times with delta yes can see the drop counters since the last time the command was run making it easier to see if counters are increasing.
show counter globalView all global counters
show counter global filter delta yesView only global counters that have changed since ran last command
show counter global name? Lists all the counters that are availables
show counter global filter categoryLists available processes such as cluster, device, dlp, flow, nat, proxy, ssl, tcp, url, etc
show counter global filter aspectLists available stages such as arp, bfd, dos, forward, offload, pktproc, etc
show counter global filter value non-zeroShow only counters without non-zero values
show counter global nameflow_policy_deny Show this one counter with a brief description
show counter global filter severitydrop Show only drop counters
show counter global filter severitydrop delta yesShow only drop counters that have happened since last command was run
Global counters can be narrowed down to specific traffic flows by using the same filters that packet captures use. Before starting is best to clear all counters and unmark any sessions that were marked by the previous filter.
debug dataplane packet-diag clear allClear all capture settings, counters and filters
debug dataplane packet-diag clear filter-marked-session allUnmark any sessions that were marked by previous filters
debug dataplane packet-diag set filter match destination8.8.8.8 Configure upto 4 filters
debug dataplane packet-diag set filter match source8.8.8.8
show counter global filter deltayes packet-filteryes severitydrop Show only drop counters for flows that match this filter
Resources
Palo KB article on global counters and filtering them
Some really good info on counters and lots of other CLI show commands
Some handy cheatsheets from Mastering Palo Alto Networks by Tom Piens